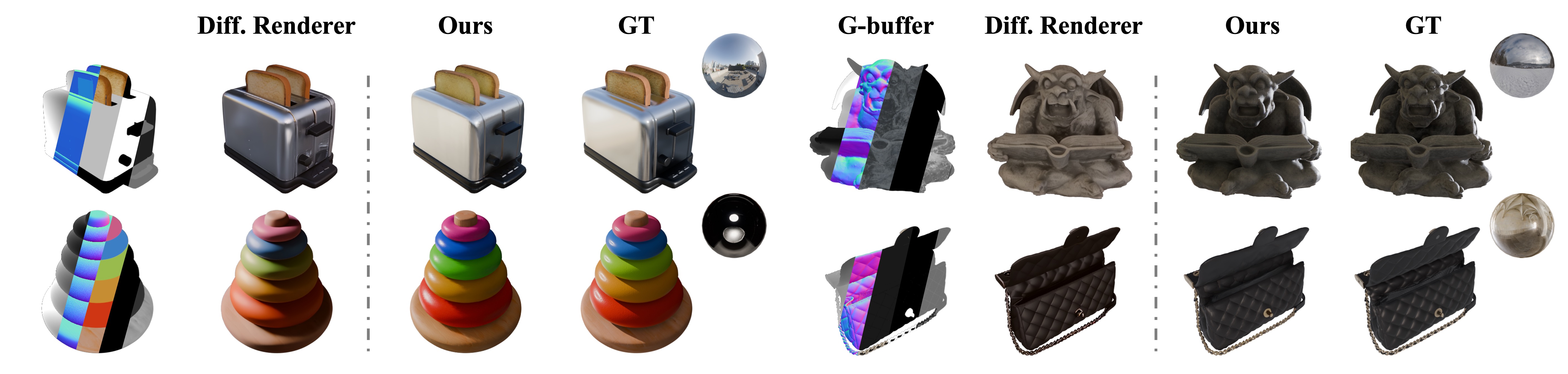
Neural asset authoring and neural rendering have emerged as largely disjoint threads: one generates digital assets using neural networks for traditional graphics pipelines, while the other develops neural renderers that map conventional assets to images. However, the joint design of the asset representation and renderer remains largely unexplored. We argue that coupling them can unlock an end-to-end learnable graphics stack with benefits in fidelity, consistency, and efficiency. In this paper, we explore this possibility with NeAR: a Coupled Neural Asset–Renderer Stack. On the asset side, we build on Trellis-style Structured 3D Latents and introduce a lighting-homogenized neural asset: from a casually lit input, a rectified-flow backbone predicts a Lighting-Homogenized SLAT that encodes geometry and intrinsic material cues in a compact, view-agnostic latent. On the renderer side, we design a lighting-aware neural renderer that uses this neural asset, along with explicit view embeddings and HDR environment maps, to produce lighting-aware renderings in realtime. We validate NeAR on four tasks: (1) G-buffer–based forward rendering, (2) random-lit single-image reconstruction, (3) unknown-lit single-image relighting, and (4) novel-view relighting, where our coupled stack surpasses state-of-the-art baselines in quantitative metrics and perceptual quality. We hope this coupled asset-renderer perspective inspires new graphics stacks that view neural assets and renderers as co-designed components instead of independent ones.
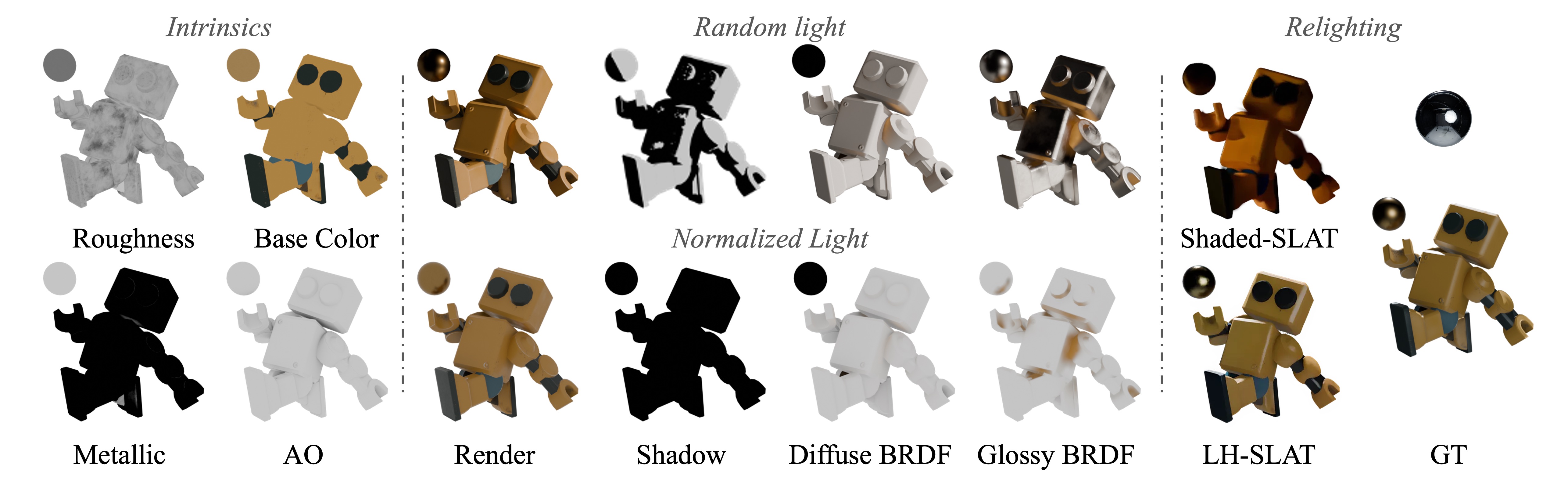
Pipeline of NeAR. Top: Light Homogenization extracts a Lighting-Homogenized Structured 3D Latent (LH-SLAT) from a casually lit input image. The right side shows the pipeline for generating LH-SLAT from a single image: we first recover a shaded SLAT, then perform illumination homogenization in voxel space. Bottom: Relightable Neural 3DGS Synthesis generates a relightable 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) field conditioned on the LH-SLAT, target illumination, and target viewpoint. The decoded 3DGS encodes geometry, appearance, and light–material interactions, and is rendered into the final relit image.



@article{li2025near,
title={NeAR: Coupled Neural Asset-Renderer Stack},
author={Li, Hong and Ye, Chongjie and Chen, Houyuan and Xiao, Weiqing and Yan, Ziyang and Xiao, Lixing and Chen, Zhaoxi and Xiang, Jianfeng and Xu, Shaocong and Liu, Xuhui and Wang, Yikai and Zhang, Baochang and Han, Xiaoguang and Yang, Jiaolong and Zhao, Hao},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2511.18600},
year={2025}
}